Note: this post was updated on October 25th, 2023
SEO is a topic of interest for many financial advisors, and for a good reason: with the right strategy, an advisor becomes more discoverable on search engines, thereby driving more traffic and attracting more potential clients to their website.
This guide will break down the fundamentals of SEO for financial advisors – from selecting relevant keywords to target, developing content designed to drive traffic, and turning that traffic into qualified leads.
It will also go in-depth on how to invest in search engine optimization for your advisory business and provide five key strategies RIAs can implement to help unlock the power of SEO.
Key takeaways from this article:
- Integrating the key phrases valuable to your business into your website is critical for search visibility
- Properly structured headers, meta tags & URLs help tell search engines about the content on your site
- Google values high-quality content that aligns with the searcher’s intent
Table of Contents
What's SEO, and why is it important for financial advisors?
Why is ranking on the first page important?
Understanding the basics of SEO for financial advisors
Top five SEO tips for financial advisors
Tip #1: Optimize your content for low-difficulty long-tail keywords
Tip #2: Take advantage of local SEO
Tip #3: Develop blog content around a collection of long-tail keywords
Tip #4: Start establishing credible backlinks
Can financial advisors benefit from SEO?
What's SEO and why is it important for advisors?
Let’s start at the top. SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization – it’s the process of gaining visibility and traffic from organic search results in a search engine such as Google or Bing. By implementing an SEO strategy, advisors can improve their website’s positioning in search engines – potentially increasing traffic to the site and earning more qualified leads.
How does it work?
Search engines may seem like black boxes, but at the end of the day, their goal is relatively simple: to provide quality information to users. These engines' algorithms are designed to present the most relevant and helpful information possible for a given keyword or phrase. In turn, websites seek to show up in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Page) for search terms that are important to their business.
For financial advisors, SEO means optimizing your web properties to achieve maximum visibility in SERPs for the phrases your ideal clients are searching for.
The closer your website can come to answering users’ questions, providing them with actionable information, or otherwise closely matching the intent of what's being searched for, the better chance you will have of ranking on the first page for those keywords that are critical to your firm.
Why is ranking on the first page important?
According to one study, the top search result in Google has an average click-through rate (CTR) of 27.6%. Conversely, less than 1% of Google searchers click on links beyond the first page of results.
Ranking on the first page is not only beneficial for advisors seeking to be discovered by the prospects they desire to work with, but it’s essentially a requirement if you want to generate any measurable traffic to your website from organic search.
So, how do you get there?
Let’s start by defining the basics of SEO and then looking at the critical steps a financial advisor can take to improve their site’s search engine rankings.
Understanding the basics of SEO for financial advisors
What are people typing into a search engine?
When someone wants to learn about something, they go to Google for information. The words typed into a search bar can be best categorized as keywords, keyphrases, and long-tail keywords.
Keywords tend to be more general and use one to two words (financial advisor), whereas a keyphrase tends to be longer (what does a financial advisor do?). And lastly, a long-tail keyword is a highly targeted phrase. An example of a long-tail keyword/phrase would be, “Financial advisor specialized in retirement planning near me.”
How many people are using a specific keyword, keyphrase, or long-tail keyword?
To understand a term's popularity, you’ll need to look at the search volume of a keyword or phrase. The search volume is the number of search queries for a specific keyword, typically measured over a month. All you need to do is plug the term into a free tool like ahrefs or ubersuggest to see metrics like search volume.
Generally, the higher the volume, the greater the opportunity–and the competition.
Unless your site is well established, realize that it may be impossible to rank for broad finance terms, given the dominance of sites such as Investopedia, Nerdwallet, etc. To better understand which keywords are best to focus on, you’ll need to assess another metric: keyword difficulty.
What's keyword difficulty?
Your chances of ranking on the first page for a given term will depend on its keyword difficulty (KD) score. The KD metric estimates how competitive that term is (e.g., to what degree are other websites creating high-quality content and seeking to rank for the same term).
This score is generally measured on a scale from 0-100, with 100 being the most difficult. An example of a difficult keyword to rank for would be “personal financial advisor” (KD of 87) vs. an easier keyword such as “should I hire a financial advisor” (KD of 27).
If you’re an advisor interested in SEO but unsure how best to invest your efforts, this is an extremely important metric to pay attention to. Knowing how hard or easy it will be to rank will help you determine what to focus on when creating content or optimizing pages on your site – and what terms simply aren’t worth your time.
What does it mean to optimize your website?
For every page on your site, you should optimize key elements, like headers, URLs, & meta tags (more on these terms shortly). These elements help search engines learn about your site and provide key information to searchers when your pages appear in SERPs. The goal is to ensure each element contains relevant terms, aligns with your brand, and accurately represents a page's content.
What are headers?
Headers are the titles that appear in your content and are used to organize the information on each site page. Headers should be concise – something that can quickly be read and understood.
The main header on each page is known as an H1 tag or a title tag (this is what will be displayed in SERPs). Your subheadings should have H2 tags, sub-sub-headings H3s, and so on. Including keywords and phrases that people are searching for in your headers makes it easier for Google to find that information when it crawls your site. This structure also benefits readability, allowing users to better digest the content on a page and understand what it contains.
What makes a good URL?
A good URL contains a high-value keyword or phrase and describes what that page covers in simple language—for example, altruist.com/become-an-ria.
For any URL you create, keep things simple. Don’t overcomplicate it with unnecessary keywords or use special characters. Only use terms relevant to the site because search engines also look for keywords in URLs.
How do you optimize title tags & meta descriptions?
Meta tags are descriptive elements that help search engines recognize your content and display a preview of it for users. These tags (including a page title and description) are invisible on the site, only appearing when your pages appear in Google results. Title tags and meta descriptions should accurately explain what’s on the page and entice users to click on the result.
What does this look like in practice? At the risk of getting too meta, here’s the SERP result for this page:
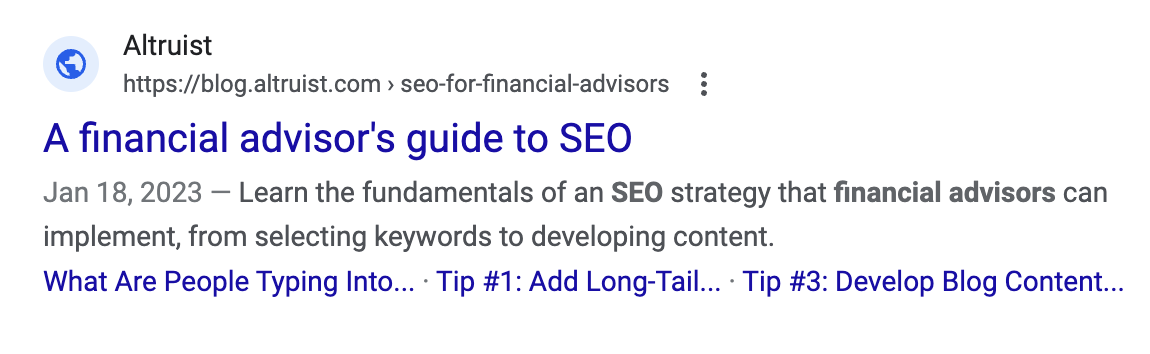
If you’re using a CMS platform like Hubspot, WordPress, Wix, etc., you should have a dedicated section for adding title tags & meta descriptions.
The page title will appear as the headline in a search result and should be limited to 60 characters or less – anything beyond that may be cut off when viewed in a SERP.
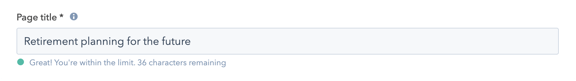
Similarly, your meta description should stay under 160 characters to avoid getting truncated. Try to include at least one relevant keyword, but avoid keyword stuffing (inserting as many keywords into one space simultaneously).
A quick tip: if you’re struggling to develop “click-worthy” descriptions, see what your competitors are doing or try ChatGPT to create some ideas.
What’s search intent and why does it matter?
Search intent is understanding why someone is searching for something – and how that search may fit your business goals. There are four primary categories of intent: Informational, Transactional, Commercial, and Navigational.
Informational intent (I) is someone seeking more information about a topic they aren’t familiar with. An example would be, “What does a financial advisor do?” The content you create for your audience will often satisfy this intent. Content can range from blog posts, videos, podcasts, etc. Incorporating informational intent keywords into your content may have a better chance of ranking on the first page of the search results.
Commercial intent (C) can be understood as a consideration action. Someone might be curious about pursuing a product or service but wants to research and compare options. An example of a commercial intent search term would be “Best financial advisors near me.”
Transactional intent (T) is used to describe terms that indicate a user has a strong desire to convert. An example would be, “Hire an advisor.” They’re aware of the action they want to take and are looking for a concrete next step.
Navigational intent (N) is when someone wants to find a particular site or page. For example, “Altruist login.”
Understanding the intent behind a search is important because it helps advisors construct their websites and content strategy to align with their prospect pipeline. Learning the type of content prospects seek can help attract quality leads, increase engagement, and boost client conversion.
Top five SEO tips for financial advisors
Now that you have a good grasp of the basic terminology let’s walk through five search engine optimization tips financial advisors can use to harness these concepts into a successful strategy for their business.
Tip #1: Add long-tail keywords with an achievable KD and commercial intent to your website
Why is it important to incorporate long-tail keywords into your SEO strategy? First and foremost, they’re easier to rank for, and you’re more likely to get in front of the people you want to work with.
As we covered above, long-tail keywords are highly specific phrases that tend to have a lower search volume because they’re niche. The people using them are more aware of the problem they’re trying to solve and more likely planning to take tangible action. For advisors, most long-tail keywords will have a commercial or transactional intent.
Here are some examples of long-tail keywords:
- “Fee-based only advisors in [city]”
- “Best advisors for financial planning in [city]”
- “Best investment advisors in [city]”
- “Best certified financial advisors in [city]”
- “Best certified financial planners near me”
- “Fiduciary advisors specialized in [your expertise] in [city]”
How do you use long-tail keywords effectively?
First, aim to include them naturally in the content on your website. Simply adding long-tail phrases to a page is not enough to rank for those terms, and when done unnaturally or excessively, it can even make your website appear spammy. So, target the highest-value phrases and incorporate them thoughtfully into the content on your site.
For example, you might notice the long-tail keyword “Fee-based advisors for financial planning in Denver” aligns with your business and is notching significant search volume. Consider catering some content on your website to that phrase and feature it as one of your services. If any pages on your site are focused on fee-based financial planning, include those keywords in your page title and meta description.
In that scenario, you would use a title incorporating the keyword, such as: “Providing fee-based financial planning to families in Denver, Colorado.” Then, the sub-header could lean more into a value statement (e.g., “We aim to provide our clients with the best possible service to help them attain their financial goals.”). The meta description should again mention the keyword.
The examples provided above heavily feature local place names. That’s because they’re incredibly valuable search traffic qualifiers, bringing us to our next tip: incorporating local SEO into your strategy.
Tip #2: Take advantage of online directories to improve local SEO
Google frequently “localizes” search results – meaning it will provide different versions depending on where you are searching from. (If your firm is 100% virtual or serves an undefined area, this section may not apply, and you can skip to the next tip).
If you’re an advisor serving a particular city, county, or region, you’re most concerned with being visible to people near you searching for terms relevant to your business. For example, if someone in your city searches for “financial advisors near me,” – you’ll want to be on the list, right? So, how should a financial advisor approach local SEO?
First, start by creating and optimizing a Google Business profile. This is a free platform for local businesses that helps your business get discovered and can drive more website traffic and generate customer reviews.
To make the most of your profile, here’s what to include:
- Your business name
- Business address
- Phone number(s)
- A link to your website
- Hours of operation
- The specific services you offer
- Any images that relate to your business
Once your profile is created, encourage existing clients to leave reviews there to help others understand your business and the benefits of working with you – and reply proactively to those reviews.
In addition to the Google Business listing, submit or set up profiles on other directories, such as Yelp, Yellow Pages, Bing Places, etc. When adding your profile to a directory, ensure your business information is correct and consistent across all platforms – including your website.
Local SEO increases your visibility in the city you serve and can improve your overall SEO efforts. By including your URL in online directories, you get backlinks from reputable sources to your site, which search engines favor.
Tip #3: Develop blog content around a collection of long-tail keywords
Developing content that scales can be challenging, especially for keywords in the financial advice industry. However, there are ways advisors can boost their chances of finding SEO success with their content strategy.
With the help of SEMRush (or a similar tool), you can conduct keyword research and identify keywords with an actionable difficulty score.
The video below demonstrates how you can use SEMRush to find related keywords to those highly popular keywords that are hard to rank for. From there, sort by KD and pick the keywords that have the highest search volume with a low KD.
Here are some rankable examples pulled from SEMRush. These have a low KD and a search volume between 100-1000:
- "How to prepare for a recession if you are retired"
- "Retirement and estate planning"
- "Retirement planning for women"
- "Cash flow-based retirement planning"
- "What's the first step in financial planning?"
To help you format your articles to make them easier for Google to crawl, here’s a quick checklist:
- Include keywords/phrases in the headline and intro paragraph, meta tags, and URL.
- Add a "key takeaways" section at the beginning of the article.
- Make it skimmable and easy to read.
- Make it relatable, including real-life examples.
- Make sure to proofread. Services like Grammarly or Writer are excellent for editing.
- If you're using images, fill in the "alt text" with your keyword/phrase related to the picture.
- Include a CTA on every piece of content. It can be as simple as subscribing to your blog, or you want them to schedule a consultation with you. You always want to entice your visitors to take the next step.
One final thought about creating content: get to the point, and don't deviate from the question you're trying to answer for your audience. Your articles must stay on track and give users the information they’re looking for; otherwise, you risk losing their attention, and they’ll jump off the page.
Check out our Content Marketing Playbook for more helpful tips on optimizing other types of content.
Tip #4: Start establishing credible backlinks
Backlinking is when another site links to your website or a page on your site. These links are powerful signals to Google that your content is valuable and will help boost its chances of ranking. According to research conducted by Backlinko, “The #1 result in Google has an average of 3.8x more backlinks than positions #2-#10”.
How do you get another site to link to yours? For starters, the more quality content you create, the higher the chance of people linking to it. But oftentimes, simply creating good content isn’t enough – you need to help people find it.
Here are three ways to jumpstart your backlink strategy:
- Reach out to publications your audience or peers follow and offer to write a guest post on a relevant topic. In return, they may agree to link to your site somewhere on the page.
- As with Local SEO, the financial industry has networks where you can build a profile and include your website’s URL. Sometimes, these directories will allow you to link to additional pages on your site that your audience will find valuable.
- If you’ve created a stellar piece that would provide valuable context to a page on someone else’s site, reach out and ask if they would consider linking to it. The best way to approach this is to craft an authentic email that seeks to provide genuine value without being pushy. Here’s an example email for inspiration:
Hi [Insert name],
I hope this message finds you well. I’ve been following your work and recently saw your latest post about [XYZ]. I found it interesting and thought it paired well with a recent article I wrote on the topic.
Here’s a link for you to check it out, and I would sincerely appreciate any feedback you have, as I think this would be a great piece that can add additional value to your audience.
Thanks in advance, and I look forward to hearing from you.
Sincerely,
[Your name]
A couple of important points about backlinks before we move on:
Not just any backlink will do; your goal is to receive links from reputable sites. Too many links from spammy websites can actually hurt your SEO. Remember: the more reputable the source linking to your site, the better it is for your ranking.
As you may have gathered, this is a long-term SEO strategy. Backlinks are hard to get, so understand you likely won’t be getting any overnight wins. But when done right, a strategy of patience and persistence in gathering high-quality links can pay off immensely down the road.
Tip #5: Track your progress
The final piece of an ideal SEO strategy for financial advisors is to measure the performance of your efforts. Doing so helps you learn what’s working and what you need to change, optimize, or test (such as headlines, keyword strategy, etc.). You can track most of this in Google Analytics or another similar tool.
Below are the primary metrics you should monitor, and why.
Target keyword ranking
This metric measures how your pages rank for the keywords you target. Have you moved up in position after optimizing or creating new content? Is your content strategy working, or does it need to be further refined?
Organic traffic
This number shows how many people come to your site through organic search. If your SEO efforts work, you should see this number increase over time. You may need to revisit your strategy if you’re not seeing an increase.
Click-through rate (CTR)
This is the average rate people click through to your site from SERPs. It’s calculated by dividing how many clicks your site received by total impressions (the number of people who saw your pages in search results). If your CTR is low, it may indicate that your headlines or meta descriptions aren’t succeeding in grabbing searchers’ attention. In that case, testing out new versions is advisable.
Exit rates
The exit rate tells you which pages your audiences see last before jumping off your website – indicating content relevance and usefulness. If a page has a high exit rate, its content may not be sufficient for what users are searching for, so you may need to spend more time optimizing and adding valuable information.
Total backlinks
Although a longer-term metric, keeping an eye on your site's total number of backlinks can indicate how compelling your content is and how your backlink strategy is working. Ideally, this number will grow over time – especially links from valuable sites in the industry.
Altogether, these metrics will help you to understand your website’s performance and the impact of your SEO efforts.
Can financial advisors benefit from SEO?
The short answer is yes. By implementing an SEO strategy, financial advisors can improve their website's visibility on search engines and drive quality traffic to their site. Site visitors can become qualified leads, and qualified leads can become clients.
The longer answer is that the extent to which you choose to invest in search engine optimization will depend on your goals. For example, if your firm is just starting and seeking to grow your client base and AUM, directing resources toward broad SEO improvements is a great long-term investment.
On the other hand, if your firm is well established and has a solid client base, perhaps your top priority is not boosting website traffic but figuring out how to reach a specific type of client. In that scenario, there might be a few high-value terms you’d like to rank for, so you decide on a more narrow and limited SEO strategy.
Regardless of your goals, by following these SEO tips, financial advisors can more effectively reach their target audiences and increase their chances of converting prospects into clients.
Are you curious to learn more about digital marketing tactics you can incorporate into your business strategy? Check out our comprehensive guide to digital marketing for financial advisors.